Faced with regulatory observations on data integrity, safety guidelines as well as increasingly diverse product portfolios and growing cost pressures, pharmaceutical manufacturers are continuously looking for ways to improve production processes. Those turning to fully paperless by selecting the right electronic Quality Management System (eQMS) platform are now reaping the benefits, from faster and efficient processes to stronger compliance and continual improvement.
A paperless pharma operation sounds impractical or unreasonable because most of the operations use paper forms especially pharmaceutical GMP manufacturing. Paper adds complication to factory quality management system. The foundation of paperless approach is built into web-based software application for virtual manufacturing. The GAMP 5 Second Edition and the FDA’s new Computer Software Assurance guidelines prove that regulators want pharma companies to ditch paper permanently. Those pharma companies turning to fully paperless by selecting the right electronic Quality Management System (eQMS) platform are now reaping the benefits, from faster and efficient processes to stronger compliance and continual improvement.
 A post graduate in Pharmaceutical Technology with Industrial Management diploma, Mr. Kaushik Desai has a distinguished career spanning over 35 years of multifunctional experience in various leadership roles with reputed pharmaceutical companies, Hoechst (Sanofi), Wyeth (Pfizer), Johnson & Johnson, Charak Pharma and Global Pharmatech (Maiva). His areas of expertise include management of both green and brown field projects, technology transfer, plant operations, contract manufacturing, regulatory intelligence, and business development. Presently, Mr. Desai is a consultant offering invaluable services in thrust areas of Technical Due Diligence, Operational Excellence, Projects and Quality Management Systems in Pharmaceutical, Herbal and Nutraceutical sectors. His contribution to pharmaceutical profession has been recognised with Pharma Leadership Award by Indian Express Group of publications, IPA Fellowship Award and IPA Eminent Pharmacist Award.
A post graduate in Pharmaceutical Technology with Industrial Management diploma, Mr. Kaushik Desai has a distinguished career spanning over 35 years of multifunctional experience in various leadership roles with reputed pharmaceutical companies, Hoechst (Sanofi), Wyeth (Pfizer), Johnson & Johnson, Charak Pharma and Global Pharmatech (Maiva). His areas of expertise include management of both green and brown field projects, technology transfer, plant operations, contract manufacturing, regulatory intelligence, and business development. Presently, Mr. Desai is a consultant offering invaluable services in thrust areas of Technical Due Diligence, Operational Excellence, Projects and Quality Management Systems in Pharmaceutical, Herbal and Nutraceutical sectors. His contribution to pharmaceutical profession has been recognised with Pharma Leadership Award by Indian Express Group of publications, IPA Fellowship Award and IPA Eminent Pharmacist Award.
 Dr. Satish Desai, Quality Professional with 27 years of industry experience, has a strong background in Pharmaceutical Quality Management. He has expertise in various aspects such as Quality Assurance, Risk Analysis, CAPA, ISO standards, Quality Control, Analytical Development, Documentation, Auditing, Training, and Laboratory setup. Dr. Desai has contributed significantly to renowned pharmaceutical companies. He has led multi-location teams in implementing quality systems, ensuring compliance with cGMP and GLP standards, and conducting audits of manufacturing facilities. He has also contributed to the industry through publications and is currently a distinguished Pharmaceutical Consultant.
Dr. Satish Desai, Quality Professional with 27 years of industry experience, has a strong background in Pharmaceutical Quality Management. He has expertise in various aspects such as Quality Assurance, Risk Analysis, CAPA, ISO standards, Quality Control, Analytical Development, Documentation, Auditing, Training, and Laboratory setup. Dr. Desai has contributed significantly to renowned pharmaceutical companies. He has led multi-location teams in implementing quality systems, ensuring compliance with cGMP and GLP standards, and conducting audits of manufacturing facilities. He has also contributed to the industry through publications and is currently a distinguished Pharmaceutical Consultant.
Digitalization of Pharmaceuticals and Bio-pharmaceuticals help to transform the quality and efficiency of plant operations by going paperless. The transition from a paper-based plant to a fully automated Manufacturing Operations Management system accompanied by a specific goal to achieve:
-On time records and reports
-Ensured compliance with pharmaceutical manufacturing quality and reporting standards
-Standardization and streamlining of manufacturing processes and workflows
-Improved enforcement and control over plant activities and workflows
-Better performance reporting and insights
-Fewer errors in the entry of quality and production data
-Integration with existing ERP system for better inventory control
Paperless document management is based on electronic operation in the establishment and an electronic batch recording (eBMR) process that can be flexibly adapted to different processes, ranging from highly automated bulk and active ingredient manufacture to highly manual filling and finishing operations.
Merits of Paperless Pharma
-Optimum efficiency, productivity, and reliability
-Reduced time, cost, and effort for compliance
-Speediness of records and reports
-End-to-end process transparency
-Accuracy and consistency of batch records
-Faster information distribution and collaboration
-Identification and prevention of errors
-Minimised rework and investigation
-Instant analytics and trends
-Quality release-by-exception
-Data Integrity assured
Before deciding to go paperless, management need to:
a.Assess the current status
-Evaluate current state of GMP documentation and records
-Identify the types, formats, locations, and owners of documents and records, as well as the workflows, procedures, and policies that govern them
-Analyse the gaps, risks, and opportunities for improvement in existing system
-Define goals, scope, and requirements for the paperless transition
b.Choose the right software
-When selecting a software solution for paperless GMP documentation and records, management should consider its functional, technical, and regulatory needs, as well as its compatibility, integration, scalability, budget, and timeline
-The software has an Electronic Document Management System (EDMS) to create, store, access, edit, approve, and distribute pdf documents electronically
-The software should have an Electronic Record Management System (ERMS) to capture, store, access, review, and audit records electronically
-Electronic signature functionality should be available to authenticate and authorize documents and records electronically
-The software should include data integrity and security measures to ensure accuracy and protection of documents and records, as well as comply with the relevant GMP standards and regulations
Paperless system
ERP, MES and LIMS are electronic solution which enables complete paperless pharma manufacturing within regulated processes. Paperless manufacturing in the pharma industry offers several advantages like full compliance with FDA and GMP regulations on data integrity when compared to traditional paper-based procedures.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
ERP is Enterprise Resource Planning software developed by the company SAP SE. ERP software is modular software made to integrate the main functions of an organization’s core business processes into a unified system.
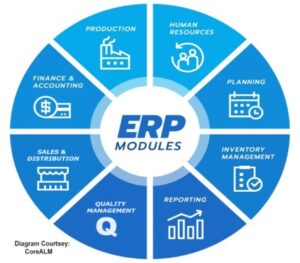 An ERP system consists of software components, called modules, each focusing on an essential business function. ERP products enable its customers to run their business processes, including Human Management, Production, Planning, Materials and Inventory Management, Sales and Distribution, Finance and Accounting, Quality Management etc, in an integrated environment, with data from each module stored in a central database. The close integration and common data store ensure that information flows from one ERP component to another without the need for redundant data entry and help enforce financial, process and legal controls.
An ERP system consists of software components, called modules, each focusing on an essential business function. ERP products enable its customers to run their business processes, including Human Management, Production, Planning, Materials and Inventory Management, Sales and Distribution, Finance and Accounting, Quality Management etc, in an integrated environment, with data from each module stored in a central database. The close integration and common data store ensure that information flows from one ERP component to another without the need for redundant data entry and help enforce financial, process and legal controls.
2. Manufacturing Execution Systems
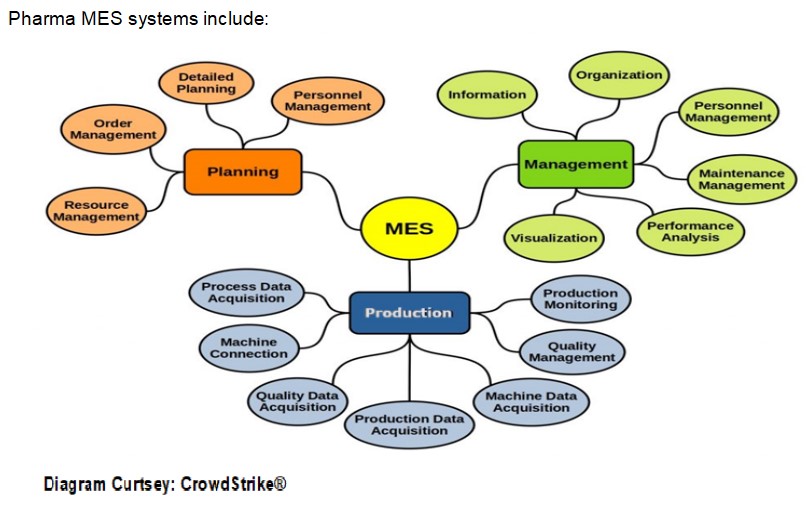
Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is a digital solution that tracks and documents the batch manufacturing process. These solutions are designed to lower costs, increase productivity, accelerate batch release, provide traceability, reduce training/upskilling time, and maintain regulatory compliance.
The implementation and integration of a fully automated robust and pre-validated Manufacturing Execution System with Electronic Batch Record (EBR) capabilities ensure a successful paperless manufacturing process fully compliant with U.S. Food and Drug Administration regulatory guidelines.
Authorized users need to design Master Batch Records (MBRs) containing all the specifications needed to automatically generate complete Electronic Batch Records for quality assurance (step-by-step processes for production, ingredients and components, verification of each step according to SOPs, electronic signatures, etc.). The system also allows the review of each batch record by exception, providing a faster and more efficient release of products. Integration with the customer’s Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solution ensures alignment between sales, planning, and operations, and facilitates resource and inventory optimization. The solution delivered would ensure manufacturing compliance with global regulatory guidelines.
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) replace paper-based, slow and error-prone processes in the manufacture of pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical products.
MES help pharma manufacturers create flawless manufacturing processes, reduce risks, time, costs, effort, and increase process efficiency and product quality. In addition, they provide valuable real-time information on requirement changes. And they are an important prerequisite for digitization and Pharma 4.0. Pharmaceutical and biotech manufacturers can reduce time, efforts and risks and finally save costs – provided that the system meets the requirements of the pharmaceutical industry in terms of functions, usability and compliance.
3. Laboratory Information Management System
Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS), a software solution, increase the operational efficiency of the laboratory by automating and streamlining the workflows, eliminating the need for maintaining information manually and meeting regulatory guidelines. A good LIMS facilitates effective management of samples, tests and associated data, record keeping and reporting, data management thus eliminating the risks of human errors due to manual entry of data and improving the overall turnaround time.
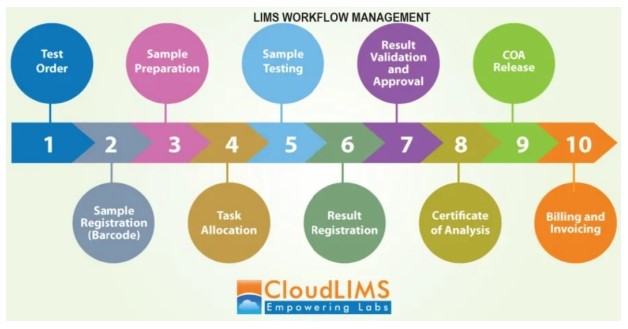 A LIMS covers the journey of a sample from its induction into a laboratory till the end of its life cycle, including the stages of Sample Storage, Testing, Automating data transfer by integration with analytical instruments, Reporting and Archiving. Once the sample is received by a laboratory, the LIMS operation starts by accessioning the sample on to the system and assigning it with a particular identification number. As and when the samples move through the laboratory, the related information can then be updated in a LIMS to maintain the audit trail. A good LIMS balances both records keeping as well as report generation. Configuring the instrument management and calibration module that is available with most LIMS products will provide the ability to interface many types of instruments with LIMS and to schedule instrument calibration and maintenance automatically, log equipment time from a central interface, or track instrument performance.
A LIMS covers the journey of a sample from its induction into a laboratory till the end of its life cycle, including the stages of Sample Storage, Testing, Automating data transfer by integration with analytical instruments, Reporting and Archiving. Once the sample is received by a laboratory, the LIMS operation starts by accessioning the sample on to the system and assigning it with a particular identification number. As and when the samples move through the laboratory, the related information can then be updated in a LIMS to maintain the audit trail. A good LIMS balances both records keeping as well as report generation. Configuring the instrument management and calibration module that is available with most LIMS products will provide the ability to interface many types of instruments with LIMS and to schedule instrument calibration and maintenance automatically, log equipment time from a central interface, or track instrument performance.
The validated LIMS and instruments with software enables integration and adheres to the ALCOA+ principles that achieves data integrity compliance in the laboratory.
Some of the core functions of a LIMS include:
-Sample Management
-Inventory Management
-Test Management
-Reporting
-Document Management
-Stability study Management
-Data Management
-Electronic Laboratory Notebook (ELN)
4. Integration of ERP- LIMS – MES
The integration between ERP, MES and LIMS enables a three-way exchange of information. The ERP is designed to integrate the MES and LIMS with various company systems including 3rd party.
System Integration involves:
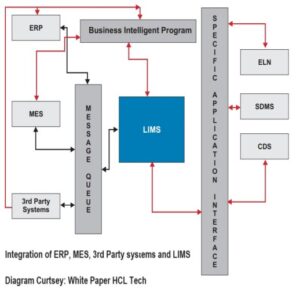 -Integrating informatic products like a chromatography data system (CDS) or an electronic lab notebook (ELN) which supports data integrity. Some system integrations are included with specific LIMS products at the time of purchase. Most of the major LIMS products have an integrated ELN and laboratory execution system (LES); some also have available scientific data management systems (SDMS). CDS providers like Waters and Agilent make integrating their systems with various LIMS quite easy to do. If LIMS has the integrations built in for systems that stakeholders plan to use, these should be integrated during the implementation.
-Integrating informatic products like a chromatography data system (CDS) or an electronic lab notebook (ELN) which supports data integrity. Some system integrations are included with specific LIMS products at the time of purchase. Most of the major LIMS products have an integrated ELN and laboratory execution system (LES); some also have available scientific data management systems (SDMS). CDS providers like Waters and Agilent make integrating their systems with various LIMS quite easy to do. If LIMS has the integrations built in for systems that stakeholders plan to use, these should be integrated during the implementation.
A relatively new option is a third-party integration platform as a service (iPaaS) product, which enables LIMS and instruments or systems like ERP and MES to integrate with one another through this platform. For complex systems, the cloud-based platform effectively acts as a pass-through for the integration messaging.
Risks of Paperless System
No electronic system can be without risk. The companies need to be prepared with fool proof system to take care of any anticipated risks. The risk could be of any of the following,
- Cyber attacks,
- Data loss risks,
- Data privacy issues,
- Environmentally damaging materials,
- Password breaches,
- Cloud system failure, and
- Protecting data integrity.
REFERENCES:
- James BlissEngineering Industries eXcellence Newsletter, Jan 18, 2021
- Nigel Bowden, Pharmaceutical Technology Europe,August 1, 2004, Volume 16, Issue 8.
- Palash Das, Paperless Documentation in Pharma, June 7, 2016
- Colin G. Thurston, Reprinted from American Laboratory ,March 2004
- JoonLeong Ng. Director at No deviation Pte Ltd., July 7, 2021
- Jonathan Boel, Articles on Paperless, QbD Group, 2022-23
- Somnath Mukherjee, White Paper, HCL Tech.
- Article by Software Services & Solutions, August 29, 2023
- Article by CloudLIMS, August 2, 2023.
- A Buyer’s Guide for Modern Manufacturing Software by ‘MasterControl’.
Rameshwar Verma on the global challenge of fighting counterfeit pharmaceuticals.
Londa Ritchey on the need for ongoing quality management engagement with CMOs.
Consistent Quality, Integrity, and Uninterrupted Supply of Medicines
By Kaushik Desai & Dr. Satish Desai
Interview
Chiranjeevi Kondapaka, CEO, Steriline Asia, speaks to Pharma Machines & Technology.
Infocus
L.B. Bohle’s BRC range of roller compactors
Reviews
Record-Breaking Showcase of Innovation and Global Collaboration in Pharm
Advancing Pharmaceutical Innovation








