For quality inspectors also, it’s a core area of interest to confirm its compliance during regulatory audits to ensure that no data integrity has occurred at any stage of product cycle. Also, cGMP violations, because of non-conformance to this clause, leading to warning letters and import alerts has already invited trouble and loss of business to many reputed drug makers in past few years.
If we think and plan to work with the prospectus of Quality by Design, then 21 CFR shall be considered as a mandatory part of URS by the customer while designing and ordering the equipment.
While discussing 21 CFR, some questions always arise in the minds of all of us, like:

For more understanding, let us go through some definitions first, as an introduction to the 21CFR Part 11 with regard to its origin and journey that was started from August 20, 1997.
If we go back to the background of this regulation, it was introduced in early 1990s by FDA on the request of pharma industry for replacement of paper record with electronic records and signatures.
What is 21 CFR?
Title 21 CFR Part 11 is part of Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations that establishes the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulations on electronic records and electronic signatures (ERES).
21 CFR Part 11 (Part 11) applies to electronic records and electronic signatures that persons create, modify, maintain, archive, retrieve, or transmit under any records or signature requirement set forth in the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, the Public Health Service Act, or any FDA regulation.
What is Title 21?
Title 21 is the portion of the Code of Federal Regulations that governs food and drugs within the United States.
Chapter I: Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
Chapter II: Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA)
Chapter III: Office of National Drug Control Policy (ONDCP)
What is Part 11?
Part 11 defines the criteria under which electronic records and electronic signatures are considered trustworthy, reliable, and equivalent to paper records.
In other words, it applies to records in electronic form that are created, modied, maintained, archived, retrieved, or transmitted under any records requirements set forth in Agency regulations and submitted to the Agency under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act and the Public Health Service Act (the PHS Act), even if such records are not specifically identified in Agency regulations.
What is the key purpose of 21 CFR?
It is the FDA’s regulations for electronic documentation and electronic signatures. It outlines the administration of electronic records in quality management system.
What controls are required to comply with 21 CFR?
a) Limiting system access to authorized individuals
b) Use of operational system checks
c) Use of authority and device checks
d) Determination that persons who develop, maintain, or use electronic systems have the education, training, and experience to perform their assigned tasks
e) Establishment of and adherence to written policies that hold individuals accountable for
f) Actions initiated under their electronic signatures.
g) Appropriate controls over systems documentation
h) Controls for open systems corresponding to controls for closed systems.
i) Requirements related to electronic signatures
What are the components of electronic records?
Under section 11.1 of subpart B (Electronic Records), all controls for closed system are clearly elaborated. The components governing control are: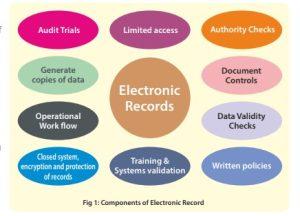
If the persons responsible for the content of electronic records also have control of system access, the system is ‘closed’. If the persons responsible for content of electronic records do not have control of system access, the system is ‘open’ (i.e., internet). Open systems require the added assurance that records are protected from point of creation to receipt.
What are the components of Electronic Signatures?
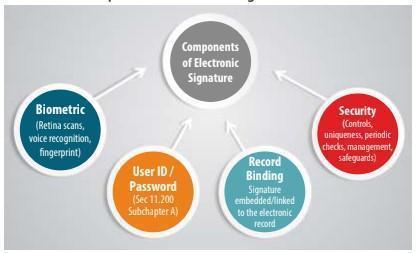
Common questions during FDA 21 CFR 11 inspection

- How can you tell who entered the data?
- How do you know which data has been changed?
- When do you lock down the data input?
- Show me some data, show me you can see the history of the data, show me you control the data life cycle.
- Is the system validated and are the requirements met?
- Can you show me the results of the validation activities?
- Does the validation include: “Pass/fail, signature, date/time stamp”; and “objective evidence – screen prints or page printouts with a link to the direction that generated the output”?
Advantages speed, audit ability and accountability
- Paperless records and collection and storage
- Data guarantees authenticity, data integrity, non-repudiation,
confidentiality of records - Electronic record audit trail availability
- Easy access to the electronic records
Summary
Part 11 compliance is now mandatory for all critical equipment with regard to enhancement of control over electronic data collection and electronic systems, vendor docs validation, audit preparation and exercising more administrative, procedural and technical controls.
In short, the key outcome of Part 11 compliance is maintaining quality and ensuring integrity.
What is an audit trail?
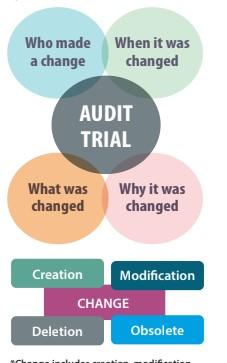
Change includes creation, modification, deletion and /or made obsolete.
An audit trail is the who, what, when, and why of a company’s data.
It’s a log containing metadata that essentially allows you to reconstruct all user actions and events involving data. An audit trail is in place to ensure the ongoing completeness, accuracy, integrity, and security of data and records. It’s also necessary to provide transparency of the actions people take with the data. This all needs to be available to auditors during an inspection. In short, the audit trail is a regulatory requirement in pharmaceutical manufacturing. You might call it a “complete history of your record keeping system.”
What happens if data is not available?
If an accurate and complete audit trail is not available, the company may not be able to pinpoint a definitive root cause of the failure and thus cannot assure itself or the regulatory authorities that it can continue to manufacture without running into the same unacceptable variation in the finished product.
What goes wrong while implementing 21 CFR?
- Non-consistency of industrial approach for software / systems development with basic requirements.
- Development function and business wing in an organisation work independently with regard to the responsibilities and management of budget.
- Business gets superseded over technical requirements because of cost implications and as a result, many critical functions are omitted by purchase as a short term savings.
- Lack of approach by industry for application of same degree of rigour and control to its management for qualification of software vendors as done in case of pharmaceutical ingredients vendor.
- Dependence and high reliability on vendor-developed and vendor-maintained software and systems regardless of what our requirements are.
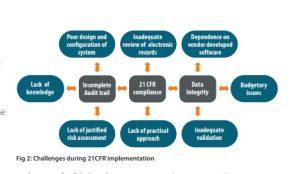
- Lack of justified and documented risk assessment” in three key areas – the need for and extent of validation, the application of audit trails, and the retention of records.
- Unlike the knowledge and capabilities that have been developed in the other
prominent industries like medical device regarding the understanding and management of risk, the pharmaceutical industry generally has much more limited experience in the formalized application of hazard control methodologies.
Conclusion
In the current scenario, correct interpretation and understanding of 21 CFR guidelines is very much required by pharmaceutical industry to reduce compliance burdens and it is high time to work with collaborative approach with FDA and other regulatory authorities seeking zero observations with regard to the compliance applying risk-based approach which is missing.
Moreover, the rationalized approach through implementation of quality culture towards betterment and optimization of systems for compliance through sanctioning of appropriate budgets, while procuring machines, will never go in trash as in return, data integrity issues and product recalls will also be eliminated from the system as a long-term benefit.
Moreover, Business always grows doing compliance!!
References:
https://www.fda.gov/regulatory information/search-fda-guidance documents/part-11-electronic-records electronic-signatures-scope-and application·
https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-21/part-11
 About the Author
About the Author
Navdeep Singh Kathuria is General Manager – Packing, Aurobindo Pharma Ltd. He is working on implementing lean methodology along with automation of process equipment. Started his career with Tablet manufacturing, his additional area of expertise is Track & Trace systems and simplification of documentation on shop floor by means of replacing manual recording into the electronic form (EBMR).